Gallstones, the problem with the gallbladder and what you can do
EDUCATE YOURSELF TO TAKE CONTROL OF YOUR LIFE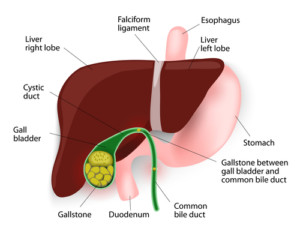
Tell me about the Gallbladder and its problems
What to do if your gallbladder has already been removed
What is a gallstone?
Gallstones form when cholesterol and bile pigments become so concentrated that they form lumps inside the gallbladder. Eighty to eighty-five percent of all gallstones are coated with layer upon layer of waxy-looking cholesterol, although many stones are coated with both cholesterol and bile pigments. A few are made exclusively of yellowish-green bilirubin a substance that is part of the hemoglobin in your blood.
What causes gallstones?
The incidence of gallstones in the American population is high and increases with age. There seems to be a familial predisposition to gallstones, but it is difficult to say whether there is truly a genetic factor since most family members usually have similar dietary habits. Diabetics have a higher incidence of stone formation and women are more commonly affected than men and the incidence increases with pregnancy.
As we said above, normally, the gallbladder is a storage compartment for the bile that your body needs to digest fat. You eat fat, the stomach sends it through to the small intestine, and your gallbladder squirts some bile onto your food to break up the fat. Your body then finishes its digestive process, and everything heads for the exit. But occasionally something breaks down during the eat-squirt-exit process and the gallbladder’s sludge-like contents crystallizes. This provides the opportunity to layer thicker and thicker coats of cholesterol or bilirubin around a calcium speck, thus forming a gallstone.
Exactly what causes this buildup of cholesterol or bilirubin on the calcium is not totally clear and there are many theories. Supposedly, it is from a high fat-high cholesterol diet. This popular belief may be far less popular and far less believable when evidence of animal experiments is presented. *
1) There is some evidence that a deficiency of vitamin E may bring this on. It was shown that animals given large amounts of cholesterol or saturated or unsaturated fats developed no stones as long as vitamin E is adequate.
Of course, today’s fast-food diet does not contain a lot of vitamin E. Check any of the nutritional listings from a fast food restaurant and see if there is any vitamin E listed.
It is believed that in the absence of Vitamin E, Vitamin A is quickly destroyed and without Vitamin A millions of dying cells from mucous membranes covering the walls of the gallbladder slough off into the bile, and that stones form around a base of organic material. It appears that these dead cells catch and hold cholesterol.
This theory about gallstone formation holds that dead cells from the gallbladder’s inner membrane act as a nucleus around which stones form. But why doesn’t this happen when vitamin E is plentiful? Vitamin A protects the integrity of skin and internal membranes. However, without enough vitamin E to guard it, vitamin A is attacked by oxidation, permitting membrane cells to die and drop into the bile
2) Stones are formed when a grain or two of calcium arrives in the gallbladder and hangs around long enough to become coated with either cholesterol or bilirubin. In other words, they form when there’s too much cholesterol in your bile. This excess forms tiny “seeds” that start out the size of a grain of sand, but can grow to the size of a marble, olive, or even an egg.
3) Naturally occurring female reproductive hormones are known to encourage that process by delaying gallbladder emptying, such as during pregnancy and dieting.
4) There is also research that shows that gallstones will also form when fat intake is low. The reasoning is that the gallbladder will not contract unless fat is taken in and if it does not do so, the bile salts will crystalize and combines with bile in the gallbladder to form stones. The scientific name for the reason stones form is “biliary stasis.”
5) Another theory is that stones are less likely to form from cholesterol when there is a high content of lecithin, which homogenizes cholesterol – also fat – and holds it in this condition.
6) Other research says that it appears that the problem underlying gallstones is related to a deficiency of hydrochloric acid or to food intolerance.
Taking all these theories together, find out
Gall stone symptoms
What are the symptoms of gallstones?
The American Medical Association Family Medical Guide (Random House) says that a million new cases of gallstones occur each year. If blockage of bile flow persists for long, many complications can occur – obstructive jaundice, infection of the gall bladder and inflammation when the trapped bile stagnates.
People with gall stones may experience only fatty food intolerance with mild pain, acid reflux symptoms or diarrhea after a fatty meal. The stone rarely causes symptoms if they remain in the gall bladder.
Gallstones cause symptoms when it interferes with normal gallbladder function by passing out of the gallbladder and getting stuck in one of the bile ducts.
Pain in the upper abdomen or near the shoulder blades, along with vomiting and nausea, occurs when the stone gets stuck in the gallbladder’s duct. The pain usually lasts a few hours, until the stone drops back into the gallbladder. If it stays stuck in the duct, a stone can block the flow of bile and cause damage to the liver, pancreas or gallbladder.
If the gallbladder becomes inflamed, it causes severe pain in the upper right abdomen (under the ribcage). This may radiate around to the back. This may be accompanied by fever, nausea, and vomiting. This condition must be treated immediately. If left untreated, inflammation of the gallbladder, called cholecystitis, can be life-threatening.
If a small stone passes out of the gallbladder it may lodge in the common bile duct causing partial or complete obstruction. These symptoms are jaundice with yellow discoloration of the skin and eyes to a varying degree.
See your health care professional when – you are experiencing sharp, unexplained pain in your upper abdomen, between your shoulder blades or in your right shoulder that lasts more than 20 minutes. Your skin and the whites of your eyes turn yellow.
Other problems:
Occasionally, a person has the typical symptoms of gallstones, but may not have gallstones. They will be found to have a dysfunctioning gallbladder. Although no stones exist, the gallbladder does not contract normally in response to the ingestion of fats. Symptoms are produced when eating.
Lifestyle Recommendations
To support liver and gallbladder health avoids the excessive consumption of saturated fats and carbohydrates. For additional kidney support, drink plenty of pure water and avoid excess consumption of foods high in oxalates or oxalic acid, such as coffee, chocolate, cocoa, tea, rhubarb, spinach, and other plant foods.
RECOMMENDED:
(Here is where we have researched and found that these products do what they say they will)
Dr. Berg’s Gallbladder Formula – Gallbladder Formula contains natural ingredients to help break down gallstones and provide bile salts for bloating and digestive stress.
This formula gets results.
Concerned with how to balance your Diet so that a gallstone doesn’t get created? Understand diet and how you can build health through your nutrition. Do you need to find out what you need to do for heathy eating? We have found a program to educate you. There’s a lot of false information out there about nutrition. Find out the true, science-based facts that will allow you to take control of your metabolic health. Think how a vibrant immune system would have changed things in 2020. Go to Understanding Nutrition Course to get educated.
STILL HAVE QUESTIONS? EMAIL AND GET YOUR QUESTIONS ANSWERED.
What about other Gallbladder Problems
If you’ve had your Gallbladder Removed – read what to do about the problems
References:
What about other Gallbladder Problems
If you’ve had your Gallbladder Removed – read what to do about the problems
*Studies
Incidence of gallstone disease and complications.
Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2018 Mar;34(2):81-89. doi: 10.1097/MOG.0000000000000418.
Gallstone disease and its correlates among patients attending teaching hospital of North India. J Family Med Prim Care. 2019 Jan;8(1):189-193. doi: 10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_358_18.
Sign up to receive the MCVitamins Newsletter!
Up-to-date info on the latest health-related news happening in the world
(available in English only)

