Melatonin
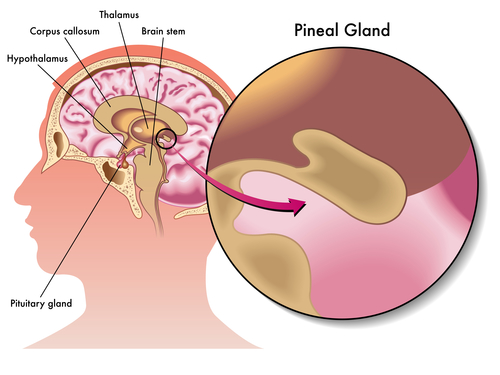 Melatonin is a natural hormone produced by the pineal gland; a pea-sized structure embedded deep within the brain. The pineal gland is the body’s natural timekeeper. The hormone melatonin is the pineal glands messenger.
Melatonin is a natural hormone produced by the pineal gland; a pea-sized structure embedded deep within the brain. The pineal gland is the body’s natural timekeeper. The hormone melatonin is the pineal glands messenger.
Sleep
Melatonin production peaks at night during sleep and falls during the day. The daily ebb and flow of melatonin controls the body’s sleep/wake cycles.
Melatonin’s main function is to help you fall asleep. When the eyes notice it’s getting dark that information gets sent to the pineal gland, which starts making melatonin. It reaches its peak at around two in the morning and then gradually tapers off toward sunrise.
Until you’re about 40, you make plenty of melatonin. As we age, our pineal gland gets smaller and produces less and less melatonin. This may be one of the reasons many elderly people don’t sleep well, or women going through menopause have trouble sleeping.
Taking melatonin supplements on a regular basis a few hours before bedtime does help some people get to sleep faster and stay asleep longer.
The supplement melatonin is supposed to help regulate the body’s sleep cycle and aid with several sleep problems, such as jet lag, insomnia, shift work sleep disorder and delayed sleep-wake phase (circadian rhythm sleep) disorder.
Research suggests that supplementing with melatonin may help people with disrupted circadian rhythms, such as people who work the night shift and people who have jet lag.
Supplementation may also help individuals sleep better who have chronically low levels, like people with schizophrenia, who have poor sleep quality.
Relieving Jet Lag
Traveling between time zones throws off you sleep rhythm as does shift work and night jobs. Melatonin can help reset your internal clock to nighttime at your destination, or new hours in a job, and helps you sleep.
Other advantages to taking Melatonin:
Animal studies have shown that adding melatonin to the drinking water of older animals can not only significantly extend life but also reverse many of the telltale signs of aging. On the basis of these studies, some researchers believe that restoring youthful levels of melatonin in humans could help prevent or slow down age-related declines in physical and mental function.
Melatonin is a potent antioxidant and free radical scavenger that can protect cells from oxidative damage. (See Free Radicals and Antioxidants)
Oxidative damage contributes to many different diseases, including Alzheimer’s disease, which is characterized by the formation of amyloid plaques in the brain that can kill brain cells. Plaques are small, disk shaped formation or growth. Amyloid is a hard protein deposit resulting from degeneration of tissue. According to a report published in the Journal of Neuroscience, melatonin has been shown in test tube studies to inhibit the oxidative damage that lead to amyloid formation in the brain, which suggests that it may help to prevent Alzheimer’s.
Another study showed that Melatonin helps relieve cluster headaches particularly debilitating headaches that primarily affect men. In a controlled study, 20 cluster headache patients were given either 10 mg. of melatonin daily or a placebo. The melatonin treatment group noticed a marked improvement after about one-month of treatment.
Melatonin has also been shown to boost immune function by activating the cancer-fighting cells that weed out potential malignancies before they can spread. A report published in the Journal of Pineal Research suggests that melatonin may help extend the life of patients with melanoma, a serious form of skin cancer. The study included 30 patients who received either 20 mg of melatonin nightly or no treatment. After 31 months, the researchers noted that the survival rate in the melatonin group was considerably better than those not receiving treatment.
For why you can’t Sleep and suggestions Sleeplessness
Sign up to receive the MCVitamins Newsletter!
Up-to-date info on the latest health-related news happening in the world
(available in English only)

